
Trase launches beef app to empower consumers in Brazil
Trase has launched a new smartphone app that informs supermarket customers in Brazil about the environmental and social performance of the meat products that they purchase.
Read in other languages:
Português brasileiroCalled Do Pasto ao Prato, meaning “From Pasture to Plate”, the app aims to address one of the biggest challenges in the food sector – the lack of transparency of food supply chains.
Some companies in Brazil’s livestock sector are linked to impacts including deforestation, human rights abuses, and poor animal welfare and hygiene standards. For example, the Brazilian cattle sector is the leading driver of tropical deforestation worldwide, and is estimated to account for a fifth of all commodity-related deforestation across the tropics.
Informing customer choice
Food retailers in Brazil provide little or no information on where the meat they sell comes from, creating a barrier for customers who want to support progress towards sustainable and ethical farming.
Trase developed the app in partnership with investigative journalists Repórter Brasil and the Belgian university, UCLouvain. The app is currently in a test phase and feedback is being sought from civil society groups and businesses across the sector. It is currently limited to beef, but there are plans to include chicken and pork. An Android version is free to download with an iOS version to be published shortly.
To use the app when shopping, a customer enters the code listed on the sanitary label commonly found on beef products and then they select the retail outlet where the product is bought. The app shows which company produced the meat and what its environmental and social performance score is according to four indicators: (1) deforestation and (2) fires in the areas supplying cattle to each slaughterhouse; (3) the fines paid by each slaughterhouse for sanitary breaches and poor animal welfare; and (4) the cases of forced labour among the slaughterhouse’s suppliers. These indicators are all based on official statistics, made accessible through the app.
“Currently, when people go to the supermarket and pick a product, the only information they have is the branding and the price,” said Dr Erasmus zu Ermgassen, a Trase researcher based at UCLouvain. “Price is clearly important – we’re currently in a moment where many families in Brazil are really struggling – but it isn’t everything.”
“Consumers want to know more,” he added. “They want to know if products are aligned with their values, if they’re sustainable or not, or come from a company with a bad track record on food safety or animal welfare. The app helps shoppers make informed choices – they can scan multiple products, compare their scores on the issues that matter to them, and then vote with their wallet.”
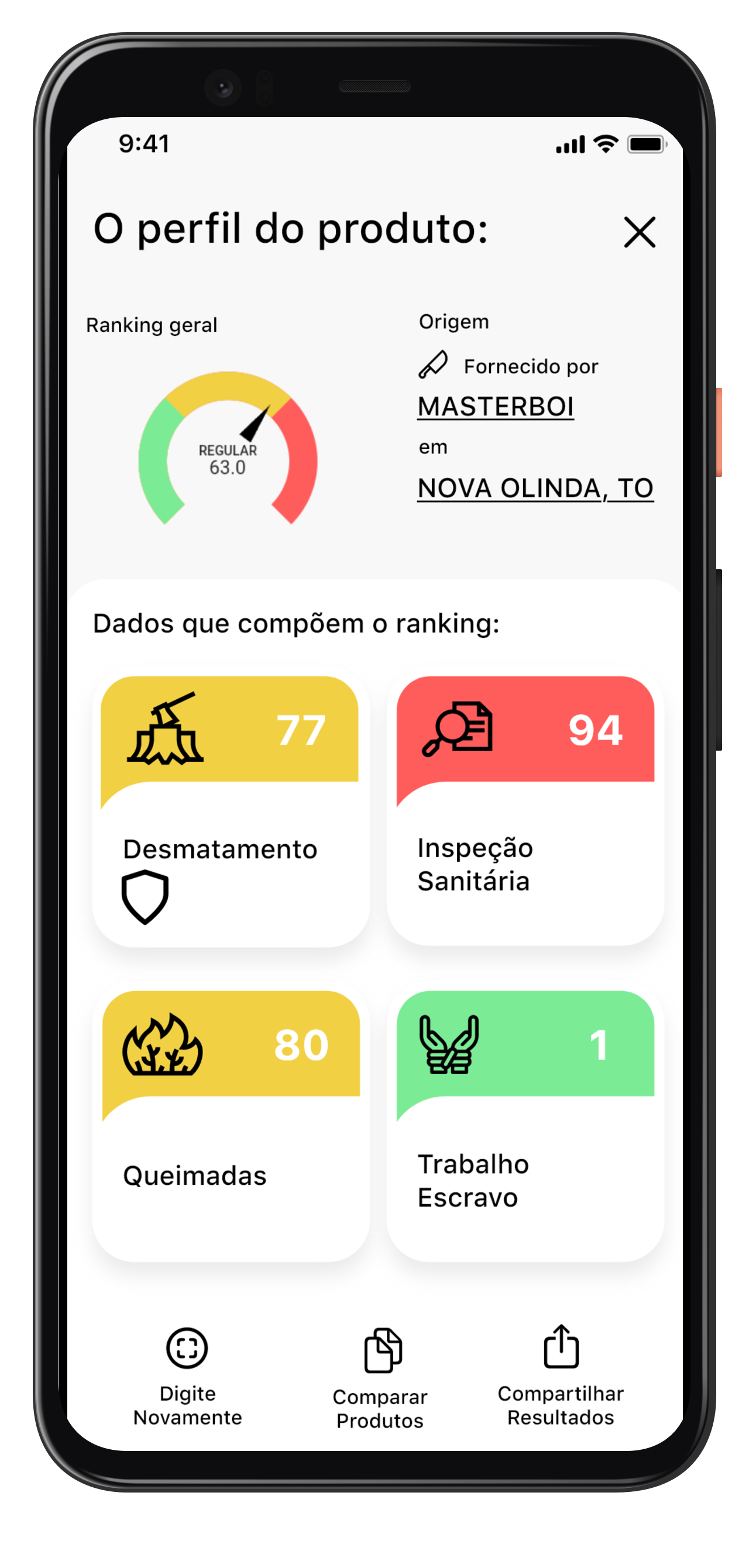
Do Pasta ao Prato screenshot
Filling the domestic data gap
The app will help Trase shine a light onto another important issue where there is a lack of information – the links between domestic meat consumption in Brazil and sustainability impacts.
Trase provides the world’s most comprehensive database on deforestation risk associated with exports of commodities such as beef and soy from producer countries including Brazil. But only around 30% of commodity production is traded internationally.
The app provides a citizen science approach – engaging the general public – to increase transparency in the supply chains of meat products in Brazil, from origin to point of sale. The information – freely available on the Do Pasto ao Prato website – will become a key resource for civil society and businesses to engage around the challenge of sustainable procurement and retail.
“The app not only raises awareness of the conditions in which meat is produced, but it also creates an unprecedented database that connects slaughterhouses to retail markets, shining a light on a previously unknown link in the supply chain,” said Dr Vivian Ribeiro, Trase indicators lead at the Stockholm Environment Institute.
“With this information, retailers can move towards better practices by bringing more sustainable products to the supermarket shelves,” she added. “This database can also be used by other stakeholders such as civil society groups, companies and universities to propose strategies on how to increase sustainability in the sector.”









